
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Under the trend of the Internet of Everything, wireless communication modules have become an integral part of all types of electronic devices, and the quality of communication of modules depends to a large extent on the rationality of antenna design. This article describes how to choose the right antenna and to play the best performance of the antenna.
With the advancement of technology, in order to save the development cycle, many manufacturers have introduced a variety of finished antennas. However, if engineers choose improperly, they will not only fail to achieve the desired results, but will waste a lot of time and cost in troubleshooting, which is not worth the candle. This article will introduce several commonly used antennas and combine their practical experience in engineering to give design recommendations for your reference.
Next we introduce the commonly used antenna types:
(1) On-board PCB antenna: It is made of PCB etching and has low cost but limited performance and good adjustability. It can be used in large quantities for Bluetooth and WiFi wireless communication modules.
(2) SMT patch type: Commonly used ceramic antennas have small occupied area, high integration, and are easy to replace. They are suitable for products with small space requirements, but this type of antenna is slightly expensive and has a small bandwidth.
(3) External rod antenna: It has good performance, requires no debugging, is easy to replace, and has a high gain. It is suitable for various terminal devices.
(4) FPC antenna: It is connected by feeders, free to install, and has a high gain. It can usually be attached to the non-metallic housing of the machine, and it is suitable for products with high performance requirements and sufficient housing space.
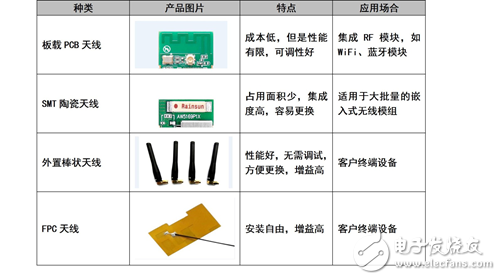
Figure 1 common antenna
The role of the antenna is to radiate radio frequency signals to free space. Selecting the right antenna at this time has a great influence on the transmission distance. The antenna is very sensitive to the surrounding environment. In many cases, even if a suitable antenna is selected, the desired effect cannot be achieved. Since some customers do not understand the factors that need to be considered in the antenna design, here we give some experience in the actual engineering design, so that customers can better design their own circuit and PCB, increase the chance of success of the project.
1, matching circuit designIn the schematic design, a π-type network needs to be reserved at the antenna and module RF output pins. The impedance of the antenna is affected by factors such as the PCB floor, antenna installation, and surrounding metal. The network is reserved to match the antenna to 50 ohms when the antenna is seriously deviated from the 50 ohm impedance.
X1, X2, and X3 are all reactance components. If the antenna is a standard 50 ohm impedance, then X2, X3 can be soldered, and X1 can be connected to 220 PF or 0 ohm. In PCB design, these three devices have been as close as possible to the RF output pins of the module, and the connected transmission lines are short and straight. Do not pave the area around the matching component within 1.5mm to reduce the effect of parasitic parameters on the matching circuit.

Figure 2 matching circuit
2, microstrip line designIn the PCB design, since most of the antenna and module output impedance is 50 ohms, in order to minimize energy reflection during transmission, the PCB lead between the RF output pin and the antenna should be a 50 ohm microstrip line. The commonly used plate is FR4 (dielectric constant 4.2-4.6). According to experience, when the line width is approximately 2.2 times the distance of the microstrip line from the reference layer, the characteristic impedance of the microstrip line is approximately 50 ohms. In the specific design, it is recommended to use the microstrip line impedance control tool (ADS, txline, etc.) to calculate, and to complete the design of the microstrip line through actual debugging. As shown in the figure below, the ground layer under the microstrip line must be a complete ground, with multiple ground vias on both sides of the microstrip line.

Figure 3 Microstrip line
3, the impact of metal on the antennaIf there is a metallic material near the antenna, the metal can reflect electromagnetic waves, which will not only affect the actual use of the antenna space, increase the loss resistance of the antenna, reduce the radiation efficiency, but also lead to deterioration of the antenna radiation performance. When installing the antenna, pay attention to:
a: At least 5mm from the battery to the antenna;
b: The antenna must be at least 4mm away from the shielding shell;
c: Do not use paint or plating with metal components on the surface of the housing when it is necessary to install the housing.
The WM6201 series is a low-power, high-performance Wi-Fi module that ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics has introduced for Industry 4.0. It is designed using Broadcom wireless solution and contains a Cortex-M4 core processor with a frequency of up to 100MHz. Wireless compliance The IEEE 802.11b/g/n protocol supports transparent transmission of the UART serial port. Users do not need to understand the complicated TCP/UDP and wireless network protocols to implement fast networking of the device.
The module is tested and certified by a series of authoritative radio frequency instruments, and uses an ultra-small volume design, making it easier to integrate into a variety of smart devices.
Email ke pemasok ini

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.